Preparing A T5 Tax Slip
Allan Madan, CPA, CA


If you’re a business owner in Canada responsible for paying dividends or other forms of investment income, understanding how to prepare a T5 tax slip is essential. The T5 is a critical document that must be filed with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) to report these payments.
This blog is designed for small business owners, accountants, and anyone involved in managing corporate finances. You’ll learn everything you need to know about preparing a T5 tax slip, from identifying the types of income that need to be reported to meeting crucial deadlines and avoiding penalties.
What is the T5 Tax Slip?
A T5 tax slip is what the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) calls the Return of Investment Income, and is used to report payments made to individuals from a corporation. These payments can include:
- Eligible dividends and dividends other than eligible dividends (including most deemed dividends)
- Bank interest; and
- Royalties
One of the most common payments is known commonly as ‘dividends’, which are distributions of profits that have been earned by the company and are paid out to shareholders.
T5 slips are prepared and provided by the company or financial institution responsible for paying out your dividends or managing your investment accounts. If an individual receives more than $50, the company or financial institution will issue a T5 slip to report the earnings.
If you yourself are the business owner, you will be responsible for filing out T5s for any shareholder that receives investment income from your company. Individuals who receive investment income from more than one company or investment account will receive multiple T5s; one for each separate entity.
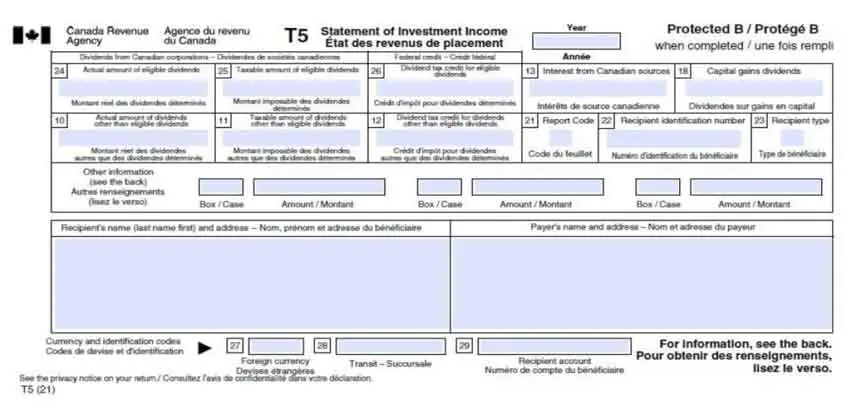
1. Be Aware of the Deadline
The T5 tax slip is due on February 28th each year. Keeping this date in mind, it’s important to ensure your company’s financial statements are prepared well in advance so you have all the necessary information to complete the slip.
The T5 form applies to the previous calendar year, which means the calculation will be made from January 1 – December 31st, despite what the company’s year-end date is.
It’s crucial for shareholders receiving dividends to have their T5 slip completed by the due date, as the information on the T5 is needed to fill out their personal T1 tax return, which is due on April 30 each year.
Missing the deadline can result in penalties, including an unreported income penalty, which is the lesser of 10% of the unreported amount or 50% of the additional tax owed.
Additionally, there is a minimum $100 late filing penalty, with the amount increasing depending on the number of slips you are required to file. These penalties apply to the person or organization responsible for filling out the T5.
2. Differentiate Dividends From Other Payments
Before you start filling out the T5, ensure that you correctly identify what constitutes a dividend. For example, shareholder loan repayments, which could be part of the initial investment, and payroll should not be reported as dividends.
Also, consider any expenses the shareholder paid on behalf of the company that have not been reimbursed. These expenses should reduce the total dividend amount. For instance, if a shareholder paid $10,000 for equipment and withdrew $90,000 from the company account, the net dividend would be $80,000.
3. Determine the Company’s GRIP Balance
The General Rate Income Pool (GRIP) balance is crucial for determining the type of dividends being paid. The GRIP represents eligible dividends received by the company and business profits exceeding $500,000 per year. This is a cumulative account, and eligible dividends paid from this account are taxed at a lower rate than ineligible dividends. This means calculating the GRIP balance is important because it can help minimize your taxes.
| Tax Rate | Taxes Paid | ||||
| Income | Type of Dividend |
Ontario | Quebec | Ontario | Quebec |
| $100,000 | Eligible Dividend |
38.92% | 39.76% | $38,920 | $39,760 |
| $100,000 | Eligible Dividend |
47.32% | 48.35% | $47,320 | $44,350 |
Table: Differing tax rates in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec for an individual in the highest tax bracket.
The moral of the story is that if you’re paying out dividends, take advantage of the company’s GRIP balance because eligible dividends have a lower tax rate.
4. Complete the T5 Slip and T5 Summary
Here are two examples to illustrate how two different business owners may fill in their T5 tax slips.
Example A
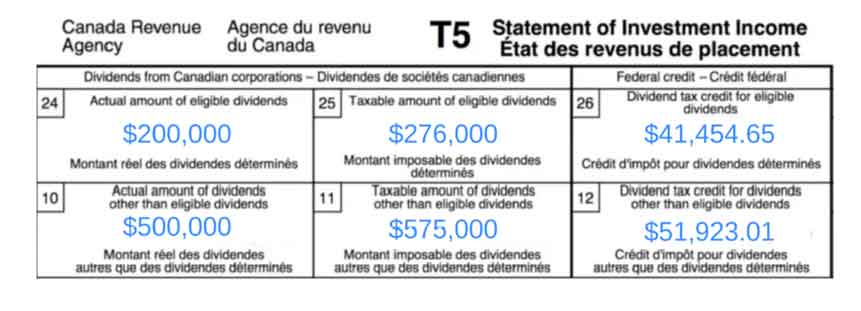
A painter who owns their own business makes a profit of $700,000. The entire profit is paid to the painter in the year. This is how they would fill out their T5 slip.
Actual Eligible Dividends: dividends paid from profits in excess of $500,000
= $700,000 – $500,000
= $200,000
Taxable Eligible Dividends: the taxation of dividends is affected by the ‘dividend gross-up’, which is 38% for eligible dividends.
= $200,000 x 1.38
= $276,000
Dividend Tax Credit for Eligible Dividends: this is calculated by multiplying the taxable eligible dividends by 15.0198%. The dividend tax credit reduces your personal income tax.
= $276,000 x 0.150198
= $41,454.65
Actual Amount of Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: These are dividends paid from profits less than $500,000.
= $500,000
Taxable Amount Of Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: this number is calculated by multiplying the actual amount of dividends (up to $500,000) by 1.15.
= $500,000 x 1.15
= $575,000
Dividend Tax Credit For Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: This number is found by multiplying the taxable amount of dividends (up to $575,000) by 9.0301%.This credit can be claimed on your personal tax return to reduce your taxes payable.
= $575,000 x 0.090301
= $51,923.01
The painter’s tax slip would look like this:
Example B
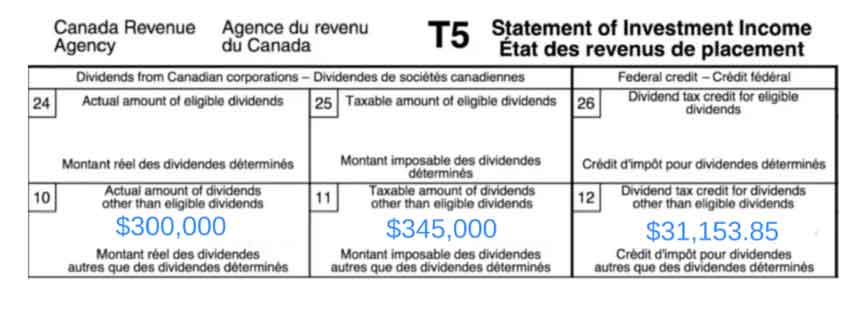
A doctor who owns their own practice receives $300,000 in dividends. The company’s profit for the year is $400,000. This is how they would fill out their T5 slip.
Actual Eligible Dividends: dividends paid from profits in excess of $500,000
= N/A
Taxable Eligible Dividends: the taxation of dividends is affected by the dividend gross-up and tax credit system, and is 38% for eligible dividends.
= N/A
Dividend Tax Credit for Eligible Dividends: this is calculated by multiplying the taxable eligible dividends by 15.0198%.
= N/A
Actual Amount of Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: These are dividends paid from profits less than $500,000.
= $300,000
Taxable Amount Of Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: this number is calculated by multiplying the actual amount of dividends (up to $500,000) by 1.15.
= $300,000 x 1.15
= $345,000
Dividend Tax Credit For Dividends Other Than Eligible Dividends: This number is found by multiplying the taxable amount of dividends (up to $575,000) by 9.0301%.This credit can be claimed on your personal tax return to reduce your taxes payable.
= $345,000 x 0.090301
= $31,153.85
The doctor’s T5 slip would look like this:
Once you have all the necessary information and calculations, you can complete the T5 slip.
- Input the recipient’s name and address
- Input the corporation name and address
- Determine if you are paying eligible dividends or non-eligible dividends. Record eligible dividends in box 24, or non-eligible dividends in box 10.
- Calculate the taxable dividend based on the formulas above
- Calculate the tax credit based on the formulas above
If you are filling out multiple T5 slips, you will then need to complete a T5 summary for your entire business. Add up all of the figures reported on each T5 slip, and ensure the year and your business number are included on the form.
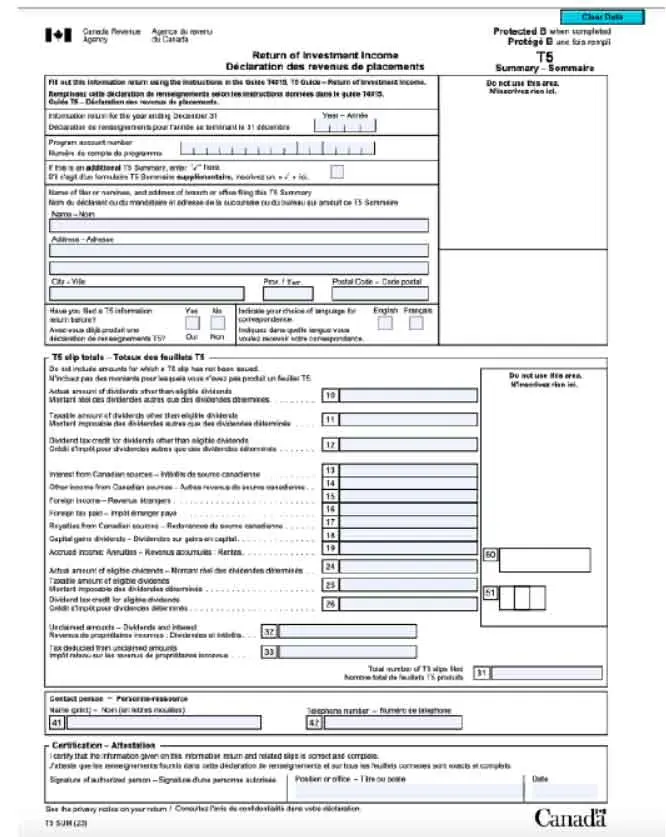
Ensure that all details are accurate and reflect the financial activity of the corporation correctly. If you need guidance on how to fill out the slip, refer to previous resources or blogs that provide detailed instructions.
5. File the T5 Slip on CRA MyBusiness Account
After completing the T5 slip(s) and summary, file them using the CRA’s MyBusiness Account portal. This online submission is efficient and ensures that your T5 is filed on time, helping you avoid any potential penalties.
By following these steps, you can prepare a T5 tax slip accurately and efficiently, ensuring compliance with CRA requirements and avoiding unnecessary penalties. If you have any questions about how to complete the T5 slip or T5 summary, please contact us.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this page is intended to provide general information. The information does not take into account your personal situation and is not intended to be used without consultation from accounting and financial professionals. Allan Madan and Madan Chartered Accountant will not be held liable for any problems that arise from the usage of the information provided on this page.



